| This research deals with the application of bifunctional resins
developed by Prof Spiro D Alexandratos for the removal of heavy metals in dilute solution.
The grafting of two active functional groups on polymers beads
(fig 2) allows some metal to be removed to a better extent than the
commercial resins (stongly acidic : sulfonic group of weakly acid : iminodiacetic group).
The metal ion enters into the polymer matrix though ion exchange (sulfonic
group) and the second functional group can precipitate or coordonate the metal.
.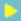 Free
radical polymerisation Free
radical polymerisation
 Polymer
functionalization Polymer
functionalization
 Polymer
caracterization (N elemental, P elemental, acid capacity) Polymer
caracterization (N elemental, P elemental, acid capacity)
 Atomic
Absorption Spectroscopy analysis. DPASV analysis Atomic
Absorption Spectroscopy analysis. DPASV analysis
 Metal
ions studies (Fe3+, Zn2+, Cu2+, A 3+, Na+...) Metal
ions studies (Fe3+, Zn2+, Cu2+, A 3+, Na+...)
|
![]() Download my résumé (PDF format)
Download my résumé (PDF format) ![]()